Supply Chain Mapping: Everything You Need to Know
Published: November 10, 2025
Last Updated: January 7, 2026

Resiliency in your supply chain is built on a clear, data-driven understanding of every link in your network. With supply chain costs consuming 10%–20% of your company’s revenue, even small changes can unlock significant bottom-line improvements and position you as a key asset to your organization. Yet many supply chain leaders lack a clear understanding of the suppliers, manufacturers, and logistics partners that power their operations. We can help you change that.
In this article, we will teach you what supply chain mapping is and how it can drive greater visibility, improve supply chain risk management, and operational success for your business. Let’s dive in!
In This Article
What is Supply Chain Mapping?
Why it Matters: 5 Key Benefits to Your Business
3 Elements of a Supply Chain Map
8 Steps to Map Your Supply Chain
4 Key Considerations in Supply Chain Mapping
5 Common Challenges & Practical Tips for Success
The Role of Technology in Supply Chain Mapping
How to get Started with Supply Chain Mapping
FAQs
WHAT IS SUPPLY CHAIN MAPPING?
Supply chain mapping is the process of gathering, organizing and visualizing each entity and activity involved in getting your product from raw materials to your customers.
This involves gathering detailed information about your direct suppliers – and potentially their suppliers – along with the logistics systems and operational processes that connect them. The result is a clear picture of where your materials are sourced, how they’re produced and transported, and who is responsible at each stage of the journey.
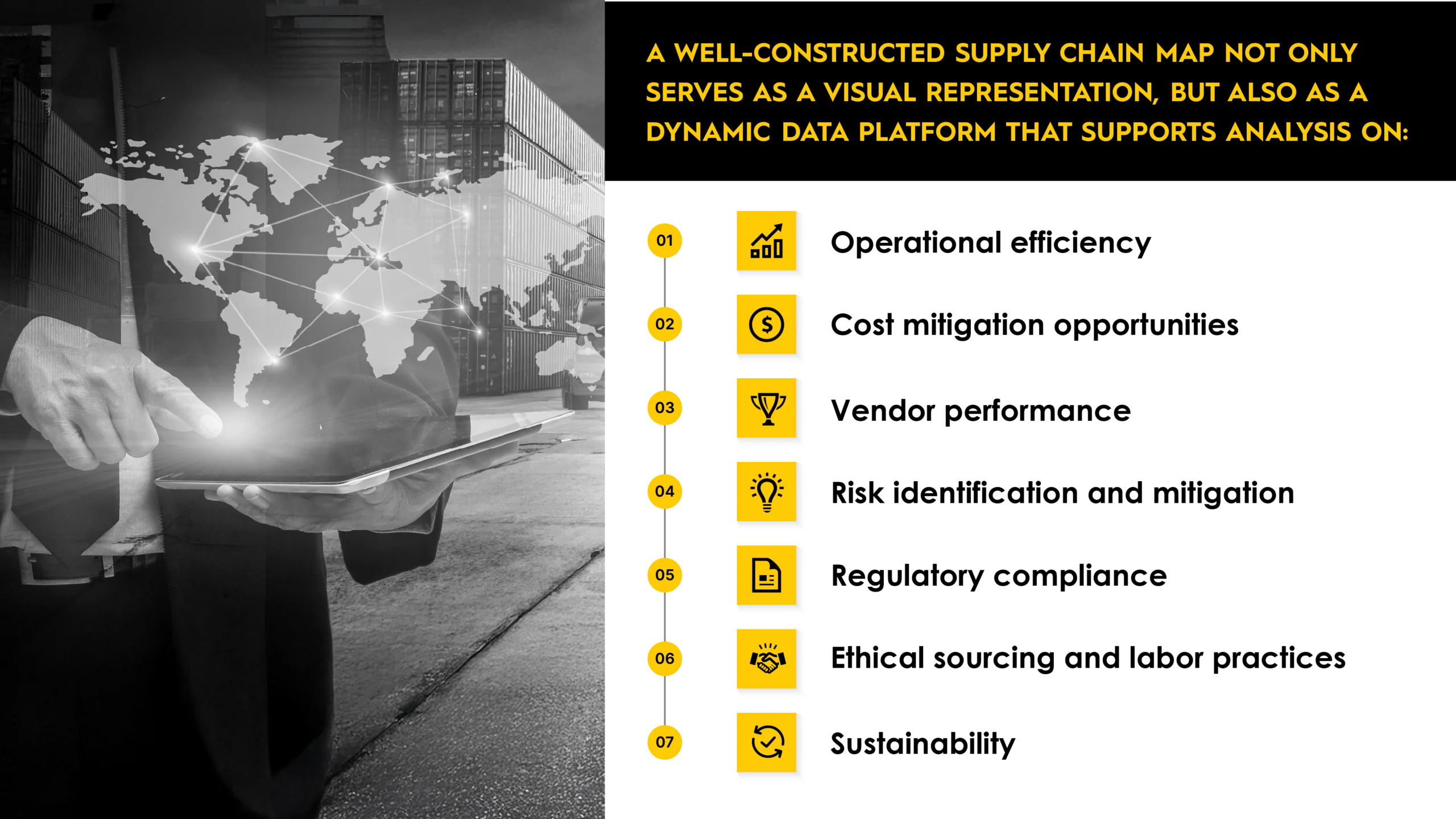
The goal is to equip you with a comprehensive visual map of your supply chain that provides critical visibility of your entire network so you can identify hidden risks, improve efficiency, ensure compliance with ethical and legal standards, and better prepare for disruptions.
Do supply chain maps need to be updated?
Absolutely. Supply chains are dynamic and ever-changing, which means your
supply chain map should be a living document – regularly updated to reflect shifts in
operations, vendor relationships, partnerships, and global conditions. Staying current
ensures you maintain visibility, reduce risk, and adapt with confidence.
Ultimately – a well-executed supply chain mapping exercise can empower you to manage complexity, make informed decisions, and build a more resilient, transparent, and responsible supply chain for your organization.
Are you ready to map your supply chain? Click here to set up an appointment!
why it matters: 5 key benefits to your business
Supply chain mapping is a foundational analysis activity that empowers you to make more informed decisions, strengthen supply chain management, and ultimately position yourself as a key contributor to enhancing, driving, and improving your organization’s profitability and success.
Here’s why it’s a powerful asset to your strategy:
1. Operational Efficiency and Cost Savings: A supply chain map will highlight inefficiencies and bottlenecks in your network allowing you to optimize logistics, reduce storage costs, improve lead times, and enhance forecasting accuracy.
2. Agility and Resilience: When disruptions occur due to natural disasters, political unrest, or supplier failure, having a well mapped supply chain will allow you to respond quickly and maintain business continuity, reducing impact on your company’s bottom line.
3. Supply Chain Risk Management: Spot vulnerabilities such as over-reliance on a single supplier, exposure to high-risk regions, or environmental threats so you can mitigate those risks before they disrupt your flow of goods.
4. Improved Collaboration: A visual, data-driven supply chain map helps teams and partners work more effectively together by aligning expectations, improving communication, and identifying your shared goals.
5. Enhanced Environmental & Ethical Performance: Supply chain mapping strengthens your ability to report on environmental and ethical supply chain metrics – helping you attract investors and meet rising expectations for transparency and sustainability. It allows you to track labor practices, sourcing conditions, and environmental impacts, reinforcing your commitment to ethical operations.
Governments are increasingly mandating supply chain due diligence to ensure legal and regulatory compliance. For example, Canada’s Bill S-211-Fighting Against Forced Labour and Child Labour in Supply Chains and the US Forced Labor Trade Law under 19 U.S.C. 1307 require businesses to demonstrate efforts to prevent forced labor. A robust supply chain map is key to achieving compliance and avoiding legal and reputational risk.
Additionally, your supply chain map supports cost mitigation and improves decision making by offering a high-level, comprehensive view of your entire supply network. This holistic perspective enhances supply chain resilience, your business’s agility, and equips you with a competitive advantage, enabling faster, more informed responses to market changes and global disruptions.
Set up your supply chain mapping consultation today!
Click here to talk to an expert!


The 3 Elements of Your Supply Chain Map
Your comprehensive supply chain map should include these three core elements:
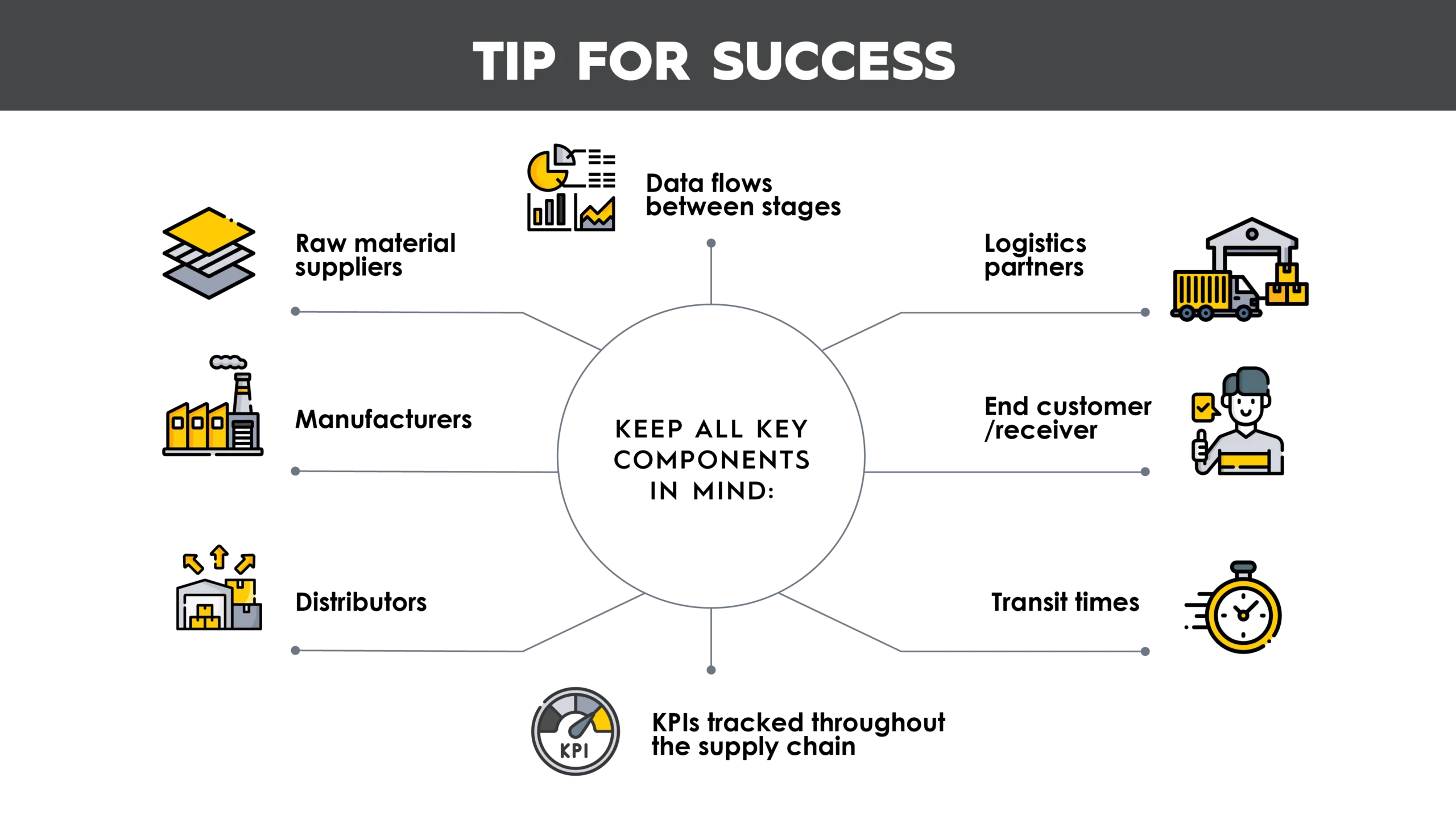
1. Partner and supplier mapping – Document the key stakeholders across all tiers, including your suppliers, logistics providers, manufacturers, and service providers. This helps you uncover interdependencies, risks, and opportunities for alignment.
2. Geographic mapping – Plot the physical locations of your supply chain nodes, including suppliers, warehouses, manufacturing sites, and distribution centers to identify routing inefficiencies and regional risks.
3. Network optimization – Identify imbalances, inefficiencies or delays that may limit your company’s flexibility or growth.

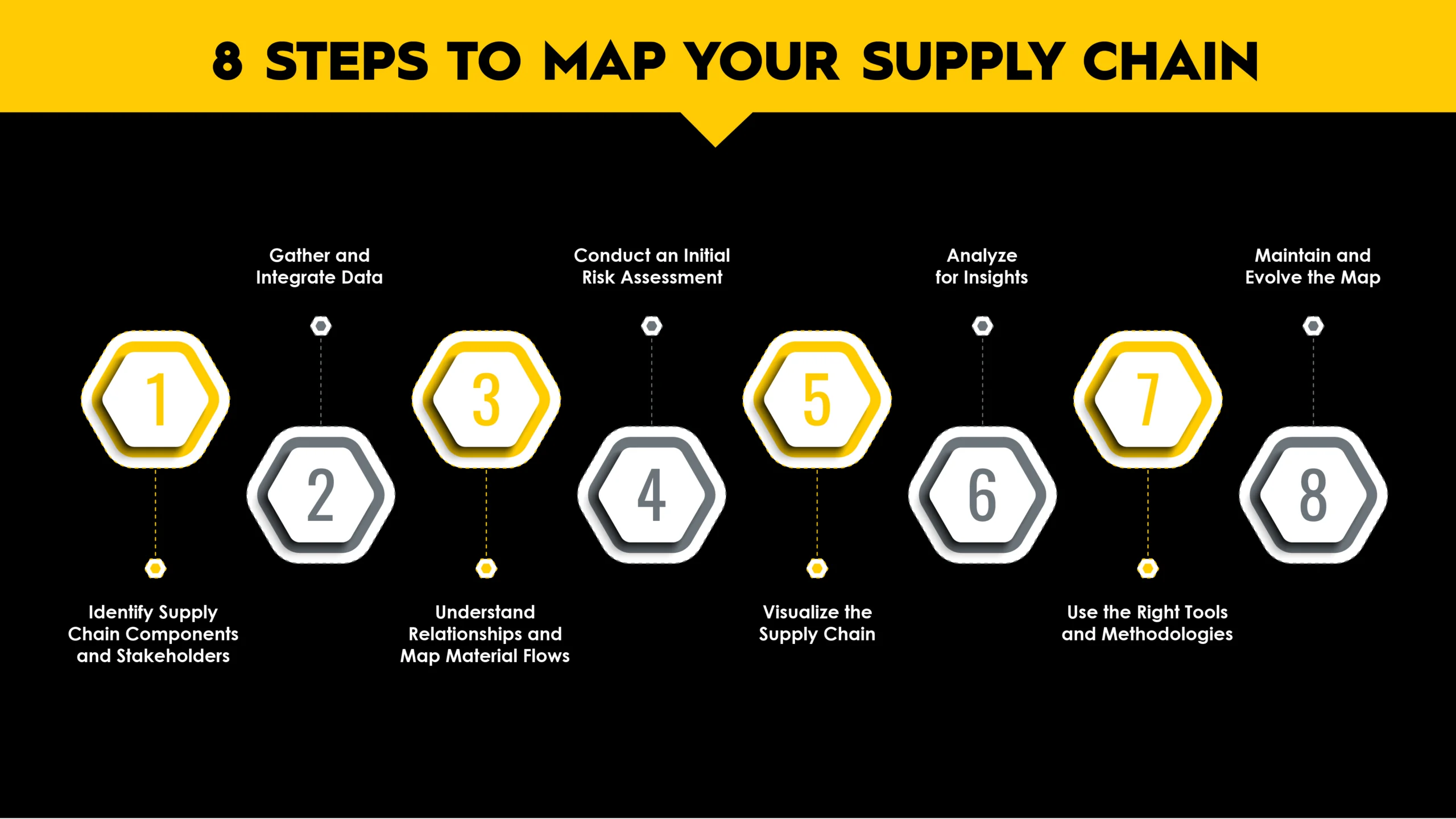
8 Steps to map Your Supply Chain
Now that we’ve covered what supply chain mapping is, why it matters, and how it benefits your business, let’s explore how to map your supply chain.
1. Identify vendors, stakeholders, and accountability
List all the key players in your supply chain, including:
- Direct suppliers and their suppliers (Tier 1, Tier 2, Tier 3, etc.).
- Vendors, manufacturers, logistics providers, and distributors
- Operational teams involved in procurement, warehousing, and fulfillment
Think through every process involved-from sourcing and production to delivery, then document the organizations and tasks associated with each step.
2. Gather and Integrate Data
Collect detailed data about:
- Supplier locations and capabilities
- Transportation methods and routes
- Production and delivery timelines
- Costs and performance metrics
- Volume levels and frequencies
Use tools like spreadsheets or centralized data platforms to consolidate this information. Make sure to pull from multiple sources, internal systems, supplier records, public data, and trade databases to ensure completeness and accuracy.
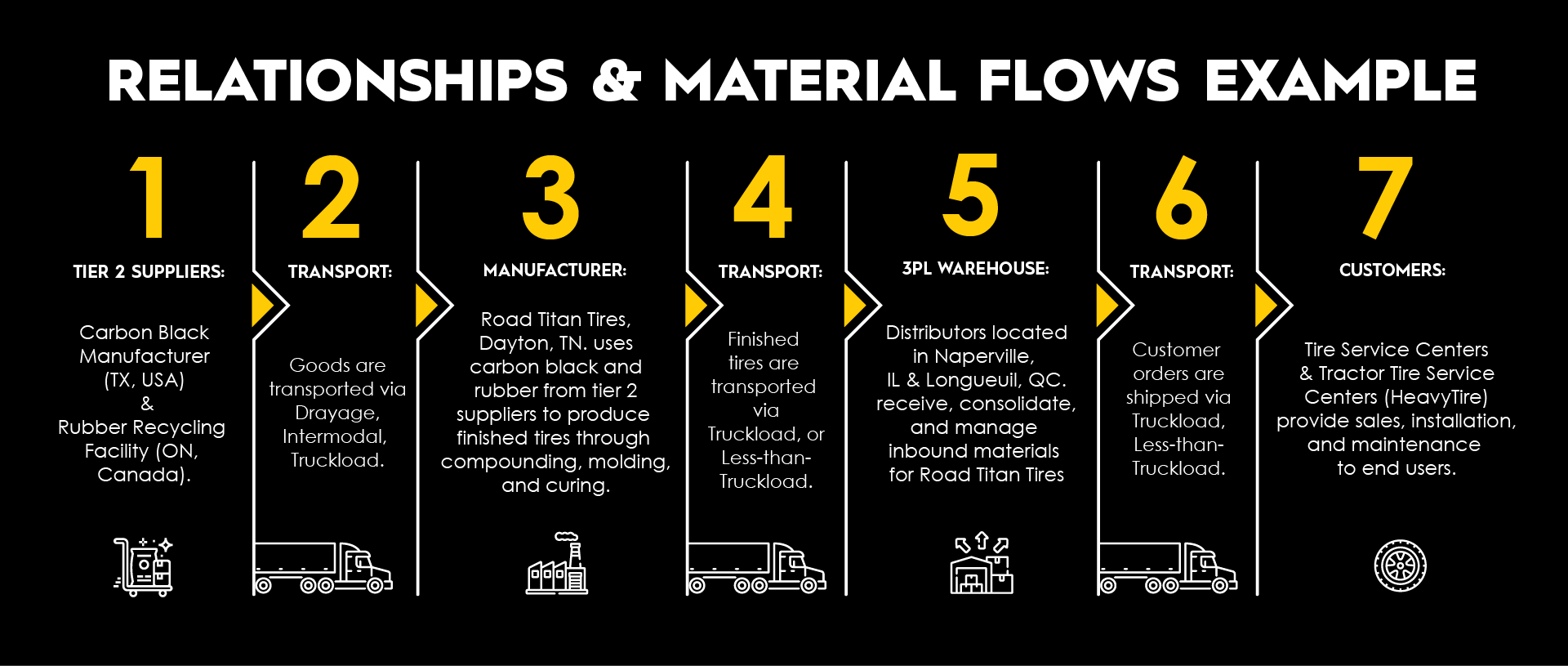
3. Understand Relationships and Map Material Flows
Organize stakeholders according to their relationships within the supply chain. For example, map how raw materials from Supplier A reach Manufacturer B, then move on to Distributor C. Track both physical movements and interdependencies.
You can code or group suppliers by tier (i.e. Tier 1: direct suppliers, Tier 2: their suppliers) and by function (i.e. manufacturing, storage, transport).
4. Conduct an Initial Supply Chain Risk Assessment
With basic relationships in place, conduct a high-level risk assessment to identify:
- Geographic or political risks tied to supplier locations
- Labor or environmental risks in specific sectors or regions
- Single-source dependencies or transportation vulnerabilities
This helps you prioritize where further investigation or action is needed – especially when addressing sustainability or regulatory compliance.
5. Visualize the Supply Chain
Create a visual map to represent your supply chain structure. This could be:
- A flowchart showing suppliers, materials, and connections
- A geographical map showing supplier locations and transport routes
- A process map that illustrates order-to-delivery workflows
Choose the format that best supports your goals – whether it’s managing risk, improving efficiency, or increasing transparency.
6. Analyze for Insights
Review your map to identify:
- Bottlenecks or delays in production or shipping
- High-cost or low-performance partners
- Duplicated or unnecessary steps
- Concentrated risks or blind spots
Use this analysis to guide improvements – whether it’s diversifying suppliers, adjusting inventory buffers, or optimizing logistics.
7. Use the Right Tools and Methodologies
Depending on your business needs, consider these mapping techniques:
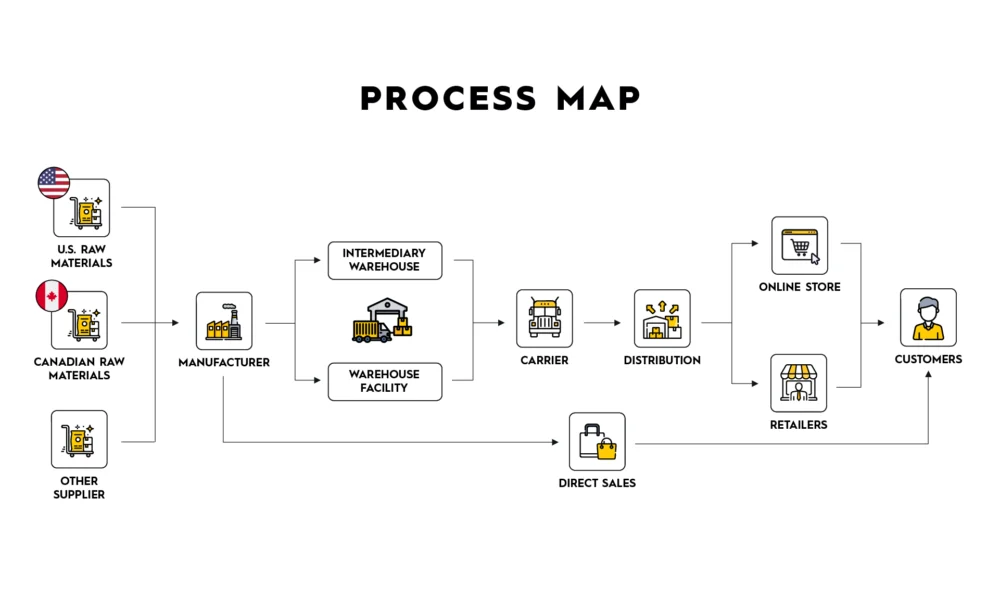
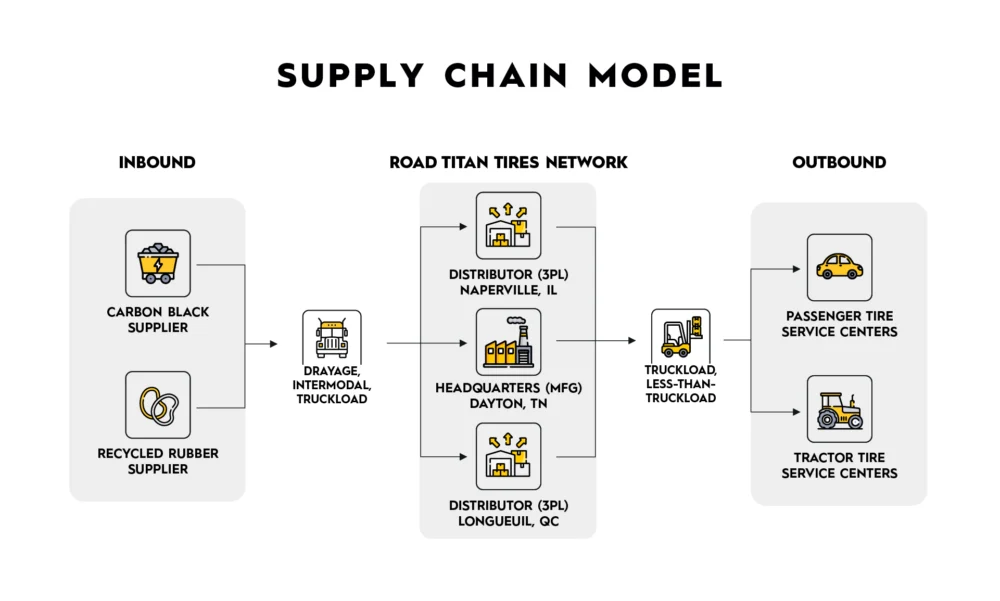
- Process Mapping: Flow of materials and products from suppliers to end customers across multiple distribution channels.
- Supply Chain Model: illustrates the movement of materials from suppliers through manufacturing, warehousing, and distribution stages, before reaching end users.
Leverage digital tools and data visualization platforms to maintain dynamic, real-time views of your supply chain.
Types of supply chain maps
8. Maintain and Evolve Your Map
Supply chain mapping is not a one-time project. Regularly update your map as suppliers change, risks emerge, and your operations evolve. Set a cadence for reviewing performance data, refreshing risk assessments, and refining visualizations.
4 Key Considerations in Supply Chain Mapping
Effective supply chain mapping is a strategic process that demands your deliberate planning and attention to several essential elements.
1. Data integration: Your organization must ensure that data from various systems, suppliers, and operations is consolidated, accurate, and current to allow for meaningful insights and responsive action.
2. Advanced technologies: The adoption of cloud-based platforms, real-time analytics, and AI-powered forecasting tools, further enhances visibility and responsiveness while reducing costs, improving efficiency and service delivery.
3. Data Synchronization: Supply chain maps should be living documents, capable of adapting in real-time to reflect evolving conditions, without causing operational downtime.
4. Sustainability tracking: As consumers and regulators increasingly demand transparency around environmental impact and ethical sourcing, it is essential that supply chain maps integrate sustainability and ethical sourcing metrics. Doing so enables organizations to effectively monitor progress and communicate their sustainability initiatives with credibility and clarity.
Ultimately, successful supply chain mapping hinges on integrating reliable data, embracing adaptable technology, and aligning with sustainability and risk mitigation strategies to build resilient, future-ready supply networks.
The right supply chain mapping partner can make all the difference – providing you with the expertise, tools, and the support needed to simplify the complexity of this important exercise, so you can stay focused on running and growing your business with confidence.
Book your supply chain mapping exercise today!

Subscribe Today!
Subscribe to receive the latest articles, newsletters, whitepapers, and industry news directly to your inbox.
"*" indicates required fields
5 Common Challenges & Practical Tips for Success
1. Lack of Real-Time Data: Outdated or manually updated systems can’t keep up with fast-moving supply chains. Without current information on inventory levels, supplier performance, or transportation timelines, your ability to make smart, agile decisions is limited.
💡 Tip 1: Digitize your supply chain processes and adopt automation tools that collect and update data in real time. This will give all stakeholders easy access to the most recent, relevant information. Talk to our team about TMS and WMS solutions today.
2. Fragmented Systems and Siloed Information: When different departments or supply chain partners use disconnected systems, it becomes difficult to create a cohesive map. Your data may be duplicated, incomplete, or difficult to retrieve.
💡 Tip 2: Designate a responsible team or individual to lead the data-gathering process. Centralize supplier information into a shared platform where it can be consistently managed and updated.
3. Poor Communication Between Partners: A lack of consistent communication among your suppliers, distributors, and internal teams can lead to misunderstandings, shipment delays, and missed opportunities to resolve inefficiencies.
💡 Tip 3: Build strong, ongoing communication routines. Regular check-ins, feedback loops, and transparent reporting will improve collaboration and reduce disruptions.
4. Supplier Transparency Issues: Some suppliers may hesitate to disclose who their own suppliers are, or where raw materials come from. This opacity makes it difficult to trace your full supply chain and assess risks like unethical sourcing.
💡 Tip 4: Use pre-screening risk tools and supplier questionnaires to gather critical data and assess environmental and/or ethical sourcing-related risks. If a partner remains unwilling to cooperate, it may be time to consider alternative suppliers.
5. Limited Visibility into Raw Material Sourcing: Not knowing where your materials originate – or how they’re handled along the chain – can hurt both your mapping accuracy and your brand reputation.
💡 Tip 5: Investigate supplier invoices, validate physical addresses via their websites, and ask specific questions about sourcing practices. Transparency at the material level is key to long-term trust and compliance.

The Role of Technology in Supply Chain Mapping
Technology and artificial intelligence (AI) are revolutionizing supply chain mapping by enhancing visibility, efficiency, and resiliency across complex global networks. AI algorithms can process vast amounts of structured and unstructured data -such as invoices, customs declarations, and logistics records – to create comprehensive, multi-tiered supply chain maps. This capability may enable your company to identify vulnerabilities, anticipate disruptions, and make informed decisions in real time.
Moreover, AI-powered tools facilitate real-time monitoring of your goods, from raw material sourcing to final delivery, by integrating data from various sources, including satellite imagery and IoT devices. Additionally, predictive analytics and machine learning models assist in demand forecasting, inventory optimization, and route planning, thereby reducing costs and improving customer satisfaction.
As supply chains become increasingly complex and susceptible to various risks, the integration of technology and AI into supply chain mapping is not just advantageous but essential. These advancements will empower your business to proactively manage risks, ensure compliance, and build more sustainable and agile supply chains.
Book a call with TRAFFIX to learn more.

How to Get Started with Supply Chain Mapping
At TRAFFIX, we make the supply chain mapping process straightforward, collaborative, and impactful – giving you the insights you need to improve performance, reduce risk, and support your growth.
Our approach starts with an open, discovery-based work session where we listen carefully to your team. By asking the right questions – about how materials move, where key activities are managed, what challenges you’re facing, and how you measure success – we build a clear and accurate view of your supply chain from end to end.
From there, we document critical insights into a comprehensive visual map, highlighting the flow of goods, key pain points, and opportunities for improvement. We organize all findings, follow up to fill in any knowledge gaps, and work closely with you to ensure we fully understand your operations before recommending solutions.
With TRAFFIX as your partner, you gain a clear, actionable roadmap to a stronger, more resilient supply chain – so you can stay focused on running your business and achieving your strategic goals.
Ready to map your supply chain? Contact us to get started.

FAQs
Supply Chain Risk Management (SCRM) is the process of identifying, assessing, and mitigating risks that can disrupt or negatively impact the flow of goods, services, and information throughout your supply chain. The goal is to ensure business continuity and minimize potential losses. A thorough supply chain mapping exercise can help you uncover risks.
Key components of SCRM include:
- Risk Identification: Pinpoint internal and external risks (e.g., supplier failure, natural disasters, cyber attacks, geopolitical issues).
- Risk Assessment: Evaluate the likelihood and potential impact of identified risks.
- Risk Mitigation and Response: Develop strategies such as diversifying suppliers, increasing inventory buffers, or implementing contingency plans.
- Monitoring and Review: Continuously track supply chain performance and external indicators to detect emerging risks.
Types of Supply Chain Risks:
- Operational Risks: Machinery breakdowns, labor shortages, or transportation issues.
- Financial Risks: Supplier bankruptcy or currency fluctuations.
- Environmental Risks: Natural disasters, pandemics.
- Political and Regulatory Risks: Trade restrictions, sanctions, or changes in regulations.
- Cybersecurity Risks: Data breaches or attacks on supply chain software systems.
Importance:
Effective SCRM can help your organization:
- Maintain product flow to customers.
- Avoid costly disruptions.
- Build resilience and competitive advantage.
- Ensure compliance with regulations.
Don’t stay blind to potential supply chain risk – Contact us to map your supply chain.
A supply chain map is essential to building supply chain resilience. For example, a company using a supply chain map may discover that 80% of a key component comes from one region in Southeast Asia. With that insight, they can proactively diversify suppliers across regions, reducing the risk of a shutdown due to regional disruption.
You can improve your supply chain resilience with:
- Increased supply chain visibility
- Risk identification and assessment
- Improved contingency planning
- Faster response to disruptions
- Better collaboration and communication
- Enhanced compliance with environmental and ethical metrics
You can enhance supply chain visibility by:
- Creating a comprehensive supply chain map.
- Digitizing your supply chain to enable live updates.
- Collecting data beyond your teir 1 suppliers as many major disruptions occur beyond tier 1.
- Integrating internal systems (e.g., ERP, TMS, WMS, CRM) with external data for end-to-end transparency.
- Use geolocation and real-time risk data (e.g., weather or geopolitical events) in your supply chain map.
- Regularly audit and update your supply chain map to maintain accuracy and support agile decision making.
- Collaborate and share sections of your map with key suppliers and partners to build trust and speed up problem solving.
With clear insights into your complex operations, your business can quickly assess exposure to international tariffs and adapt routing, sourcing, or production strategies accordingly to help avoid setbacks and delays.
Keeping your supply chain environmentally and ethically compliant involves aligning your operations and supply practices with sustainability, ethical labor standards and transparent governance. You can achieve this by leveraging supply chain mapping and risk management techniques:
- Map your supply chain to pinpoint environmental and ethical sourcing risk hotspots (e.g., factories in countries with weak labor laws)
- Define clear environmental and ethical sourcing standards by establishing a supplier code of conduct that aligns with international frameworks (e.g., UNGC, ISO 14001, SA8000)
- Screen and audit suppliers through regular audits to assess compliance with your environmental and ethical sourcing criteria.
- Digitally monitor environmental and ethical sourcing metrics across your supply chain (i.e. carbon emissions or water use).
- Build environmental and ethical sourcing metrics into procurement decisions by scoring suppliers based on performance and incorporating those scores into supplier selection and contract renewals.
Improving supply chain efficiency and enhancing customer delivery performance requires optimizing operations across sourcing, production, logistics, and data visibility. Here’s a structured approach:
- Map your supply chain end-to-end to visualize how products flow from raw material to end customer.
- Optimize inventory management balancing just-in-time (JIT) with safety stock.
- Improve demand forecasting accuracy with real-time sales data, customer trends, and external signals.
- Streamline logistics and transportation by consolidating shipments using dynamic routing and live-tracking updates.
- Work closely with key suppliers by sharing your forecasts and collaborating on capacity planning.
- Digitize and automate operations with integrated systems like an ERP, WMS, or TMS.
- Monitor KPIs and set benchmarks for order cycle time, on-time delivery (OTD), perfect order rate, etc..
- Shorten and localize supply chains where possible by nearshoring or dual-sourcing to reduce lead times and transportation delays.
- Enhance customer communication by providing real-time order tracking, delivery estimates, and automated alerts.
Ready to enhance your delivery performance? Book your supply chain mapping session today!
Reducing your supply chain costs requires a strategic mix of process optimization, technology adoption, smarter sourcing, and data-driven decision-making.
- Map your supply chain to find cost hotspots.
- If possible, optimize your supplier base by consolidating purchases with fewer, high-volume suppliers, negotiating better terms, or switch to lower-cost regions factoring in risk.
- Reduce transportation costs by partnering with a reliable 3PL that can offer multi-modal solutions, consolidations, container optimization, and other customized solutions based on your business needs.
- Improve manufacturing efficiency using Lean or Six Sigma principals.
- Streamline inventory and warehousing with the right inventory management strategy and automated warehouse operations.
- Adopt digital supply chain tools that offer analytics, real-time tracking, etc.
- Track and benchmark key cost metrics such as cost per unit delivered, inventory carrying costs, etc.
- Automate repetitive processes like invoicing.
- Reduce waste and improve sustainability by using recycled materials, optimizing routes, and reducing packaging where feasible.